The Intersection of Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence in Supply Chains
Understanding Blockchain and AI Basics
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that records transactions across many computers. This technology ensures that entries cannot be altered retroactively, making it an ideal solution for secure data management. On the other hand, artificial intelligence (AI) refers to computer systems that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as decision-making and problem-solving.
Blockchain is the technology that allows you to create a digital ledger of transactions, so you can have transparency and trust among multiple parties.
When we combine blockchain's transparency with AI's analytical capabilities, we create a powerful synergy that enhances supply chain operations. For instance, AI can analyze vast amounts of data stored on a blockchain, providing insights that lead to better decision-making. This duo not only boosts efficiency but also fosters trust between supply chain partners.
Understanding these technologies is crucial as they lay the groundwork for innovative applications in supply chains. By grasping the basics of blockchain and AI, businesses can unlock new opportunities and address existing challenges in their operations. This sets the stage for exploring their intersection in detail.
The Role of Blockchain in Supply Chain Transparency
One of the standout features of blockchain is its ability to enhance transparency within supply chains. Every transaction recorded on the blockchain is immutable and accessible to all authorized parties, allowing for real-time tracking of products. This level of transparency helps in verifying the authenticity of goods, which is particularly vital in industries like pharmaceuticals and food.

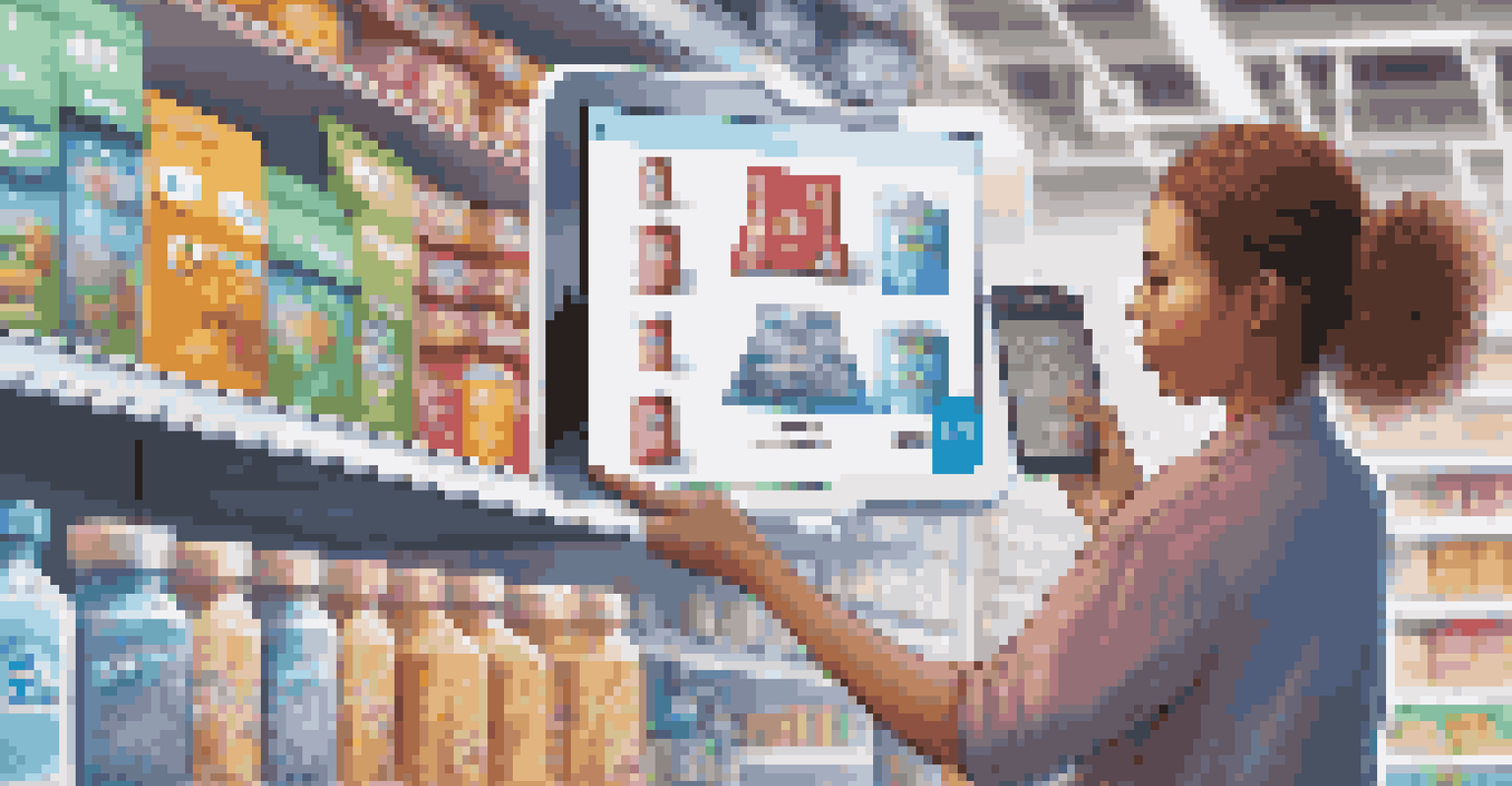
For example, imagine a consumer wanting to know where their organic tomatoes came from. With blockchain, they can trace the entire journey from farm to table, ensuring that what they buy is indeed organic. This not only builds consumer trust but also holds suppliers accountable for their claims.
Blockchain Boosts Supply Chain Trust
Blockchain enhances transparency in supply chains, allowing stakeholders to verify product authenticity and track transactions in real-time.
Moreover, increased transparency can help businesses identify inefficiencies or issues in their supply chains more quickly. By having a clear view of the entire process, stakeholders can make informed decisions to rectify problems, ultimately enhancing overall supply chain performance.
How AI Enhances Decision-Making in Supply Chains
Artificial intelligence plays a crucial role in streamlining decision-making processes within supply chains. By analyzing historical data, AI systems can predict future trends, helping businesses manage inventory more effectively. For instance, an AI tool can forecast demand for a product based on seasonality and consumer behavior, preventing overstock or stockouts.
Artificial intelligence is the new electricity. Just as electricity transformed industry after industry, AI is going to do the same.
Additionally, AI can optimize logistics by analyzing various factors, such as traffic patterns and weather conditions, to suggest the most efficient routes for deliveries. This not only saves time but also reduces costs and carbon emissions, aligning with sustainable practices.
By integrating AI into supply chain operations, companies can make data-driven decisions that enhance efficiency and responsiveness. This dynamic capability allows businesses to adapt to changes in the market quickly, maintaining a competitive edge.
Combining Blockchain and AI for Enhanced Security
The intersection of blockchain and AI significantly boosts the security of supply chains. Blockchain's decentralized nature makes it incredibly difficult for malicious actors to alter data without detection. When AI is applied, it can continuously monitor transactions and flag any anomalies, providing an additional layer of security.
For example, if an AI system detects unusual patterns in transactions—like an unexpected surge in the purchase of a specific product—it can alert stakeholders to potential fraud. This proactive approach to security not only protects businesses but also safeguards consumers from counterfeit products.
AI Streamlines Decision-Making
By analyzing historical data, AI helps businesses predict trends and optimize logistics, improving inventory management and operational efficiency.
Together, blockchain and AI create a robust security framework that ensures the integrity of supply chain data. As cyber threats become more sophisticated, these technologies offer a vital solution for companies looking to protect their assets and reputation.
Improving Supply Chain Efficiency with AI and Blockchain
Efficiency is a key goal for any supply chain, and the combination of AI and blockchain can significantly enhance operational processes. By utilizing AI to analyze blockchain data, businesses can identify bottlenecks and streamline workflows. This leads to faster decision-making and improved resource allocation.
For instance, AI algorithms can assess the performance of suppliers based on historical blockchain data, allowing companies to choose the best partners. This not only optimizes procurement strategies but also fosters stronger relationships with reliable suppliers.
Additionally, the automation of repetitive tasks, such as data entry and order processing, frees up valuable time for employees to focus on strategic initiatives. The result is a more agile and responsive supply chain that can adapt to changing market conditions.
Challenges in Implementing Blockchain and AI
While the benefits of combining blockchain and AI in supply chains are significant, there are challenges to consider. One major hurdle is the integration of these technologies into existing systems. Many companies may have legacy systems that are not compatible with blockchain, requiring a significant investment in technology and training.
Furthermore, the lack of standardized protocols in blockchain can lead to fragmentation, making collaboration between supply chain partners more complex. Without a common framework, achieving seamless data sharing and interoperability becomes a daunting task.
Combining Tech Enhances Security
The synergy of blockchain and AI provides a robust security framework that protects supply chain data from fraud and cyber threats.
Lastly, there are concerns related to data privacy and compliance. Companies must ensure that their use of AI and blockchain adheres to regulations while protecting sensitive information. Addressing these challenges is crucial for realizing the full potential of these technologies in supply chains.
Future Trends in Blockchain and AI for Supply Chains
As technology continues to evolve, we can expect exciting developments at the intersection of blockchain and AI in supply chains. One emerging trend is the rise of decentralized supply chain networks, where independent entities collaborate using blockchain to share data securely. This could lead to more resilient and adaptable supply chains.
Another trend is the increasing use of smart contracts powered by AI, which automate transactions based on predefined conditions. For instance, a smart contract could automatically release payments when goods are delivered and verified on the blockchain, streamlining financial processes.

Finally, we may see more focus on sustainability, with AI and blockchain enabling companies to track and verify environmentally friendly practices throughout their supply chains. This aligns with the growing consumer demand for ethical sourcing and could reshape supply chain strategies for the better.