Digital Twin Technology: Transforming Manufacturing Industries
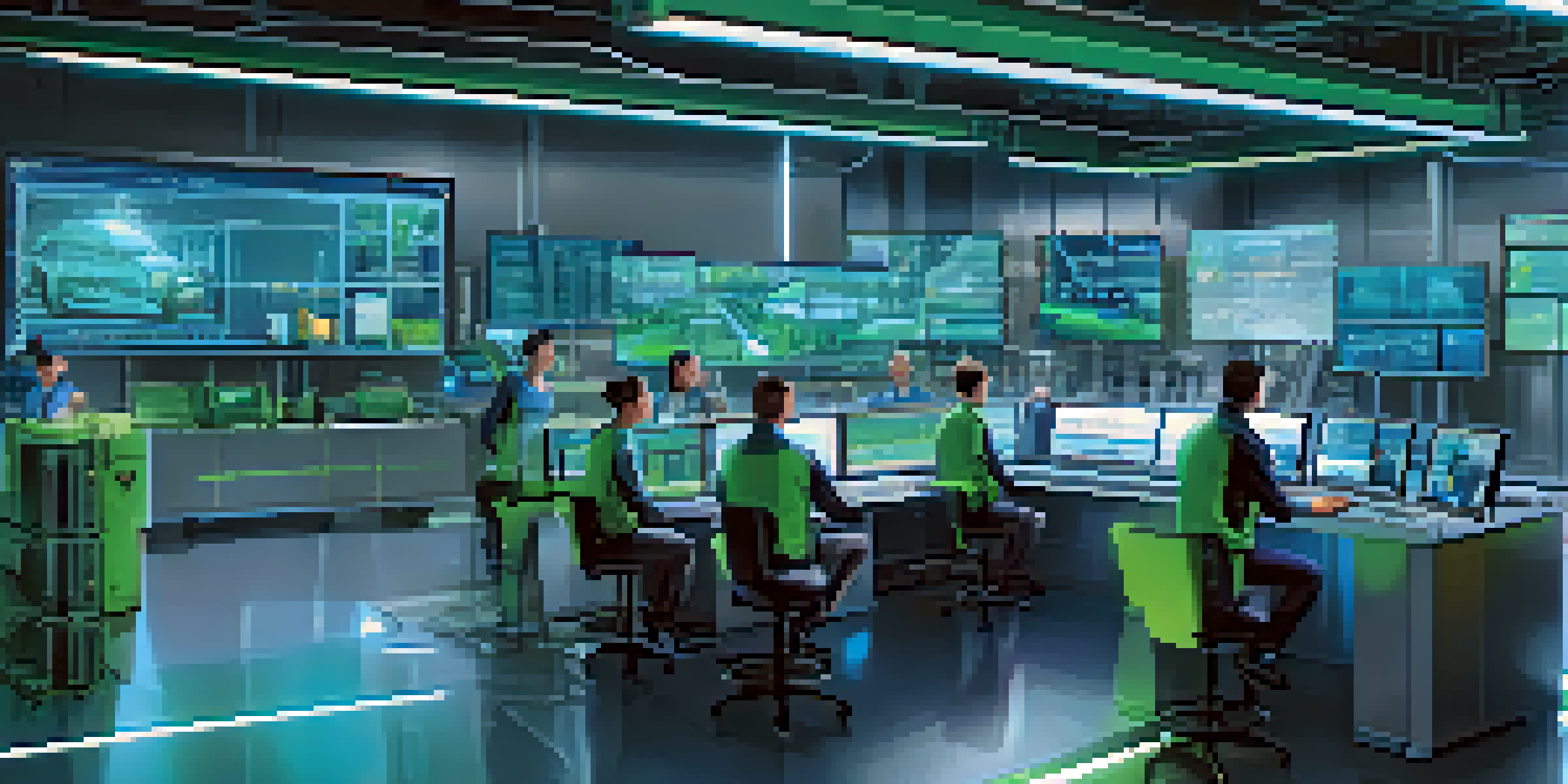

Understanding Digital Twin Technology in Manufacturing
Digital twin technology refers to the digital replica of physical entities, providing real-time data and insights. Imagine having a virtual model of your manufacturing process that reflects changes instantly—this is what a digital twin offers. It enables manufacturers to monitor and optimize operations by simulating various scenarios and outcomes.
The digital twin is a digital representation of a physical object or system that allows for monitoring and analysis in real-time.
By creating a digital twin, companies can enhance their understanding of machinery performance, product lifecycle, and even supply chain logistics. This technology bridges the gap between physical and digital worlds, making it easier to predict issues before they arise. As a result, manufacturers can make informed decisions that enhance productivity and reduce costs.
In essence, digital twins help manufacturers visualize complex processes, much like how a map helps you navigate a new city. With this clarity, teams can work more efficiently and collaboratively, leading to better overall outcomes.
Benefits of Implementing Digital Twin Technology
One of the most significant benefits of digital twin technology is improved operational efficiency. By continuously monitoring the performance of equipment, companies can identify bottlenecks and minimize downtime. This proactive approach not only saves time but also dramatically reduces maintenance costs.
Additionally, digital twins facilitate better product development by allowing for rapid prototyping and testing in a virtual environment. Instead of building multiple physical prototypes, manufacturers can simulate different designs and processes, speeding up the innovation cycle. This means faster time-to-market for new products.
Digital Twins Enhance Efficiency
Digital twin technology allows manufacturers to monitor operations in real-time, optimizing processes and reducing costs.
Moreover, the insights gained from digital twins can lead to enhanced customer satisfaction. By understanding how products behave in the real world, manufacturers can make adjustments that improve quality and performance, ultimately meeting customer needs more effectively.
Challenges in Adopting Digital Twin Technology
Despite its advantages, adopting digital twin technology comes with its own set of challenges. One major hurdle is the initial investment required for the necessary software, hardware, and training. Companies must weigh the costs against the potential long-term benefits to ensure a worthwhile return on investment.
Digital twins are the bridge between the physical and digital worlds, transforming how we design, build, and operate products and systems.
Moreover, integrating digital twin technology into existing systems can be complex. Manufacturing processes may vary greatly, and aligning new technology with legacy systems requires careful planning and execution. This integration often demands a cultural shift within the organization to embrace data-driven decision-making.
Lastly, data security is a concern as digital twins rely on vast amounts of real-time data. Manufacturers must implement robust cybersecurity measures to protect sensitive information from potential breaches, ensuring that their digital twins operate smoothly without compromising valuable data.
Real-World Applications of Digital Twin Technology
Digital twin technology is already making waves in various manufacturing sectors. For instance, in the automotive industry, companies like Ford use digital twins to simulate vehicle performance and design features, allowing them to optimize every aspect before production. This approach not only enhances safety but also improves fuel efficiency.
In aerospace, manufacturers like Boeing utilize digital twins to monitor aircraft systems in real-time, predicting maintenance needs and ensuring peak performance during flights. This application significantly reduces the risk of failures and enhances passenger safety, showcasing the technology's life-saving potential.
Challenges in Implementation
Adopting digital twin technology requires significant initial investment and integration with existing systems, posing challenges for companies.
Moreover, the consumer electronics sector has also embraced digital twins, with companies like Samsung employing them to streamline production processes and enhance product quality. By continuously refining their manufacturing methods through simulations, these companies can respond swiftly to market demands.
The Role of IoT in Digital Twin Technology
The Internet of Things (IoT) plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of digital twin technology. By connecting physical assets to the internet, manufacturers can gather real-time data that feeds directly into their digital twins. This connectivity allows for constant monitoring and analysis, enabling timely interventions when issues arise.
With IoT devices embedded in machinery and processes, manufacturers gain a wealth of information about performance metrics, environmental conditions, and operational efficiency. This data empowers them to make data-driven adjustments, enhancing overall productivity. It's like having a smart assistant that keeps you informed about every aspect of your operations.
Furthermore, the integration of IoT and digital twins paves the way for advanced automation. As machines communicate with each other and with their digital counterparts, manufacturers can implement automated responses to optimize workflows, reduce human error, and ultimately achieve a more streamlined operation.
Future Trends in Digital Twin Technology
As digital twin technology continues to evolve, several trends are emerging that promise even greater impacts on manufacturing. One key trend is the increase in artificial intelligence (AI) integration, which can enhance predictive analytics within digital twins. By leveraging AI, manufacturers can not only simulate outcomes but also predict future scenarios with greater accuracy.
Another trend is the growing emphasis on sustainability, as companies use digital twins to model energy consumption and environmental impacts. This enables manufacturers to identify areas for improvement, reduce waste, and implement greener practices. Sustainability is becoming a crucial factor in the competitive landscape, and digital twins can guide this transformation.
Future Trends in Digital Twins
Emerging trends like AI integration and sustainability focus are expected to drive the evolution of digital twin technology in manufacturing.
Finally, the democratization of digital twin technology is set to rise, making it accessible to smaller manufacturers. As costs decrease and user-friendly platforms emerge, more businesses will be able to harness the power of digital twins, leveling the playing field and driving innovation across the industry.
Conclusion: Embracing the Future with Digital Twins
In conclusion, digital twin technology holds immense potential for transforming manufacturing industries. By creating accurate digital representations of physical assets, manufacturers can enhance efficiency, reduce costs, and improve product quality. The benefits are clear, but embracing this technology requires thoughtful planning and investment.
As companies navigate the challenges of adoption, the rewards of implementing digital twins can lead to significant advancements in productivity and innovation. With the right strategy, manufacturers can position themselves at the forefront of their industries, ready to tackle future challenges head-on.

Ultimately, digital twin technology is not just a trend; it’s a fundamental shift in how manufacturing operates. By embracing this future, manufacturers can ensure they remain competitive and responsive in an ever-evolving market.