DevOps Tools: Essential Software for Continuous Integration

Understanding Continuous Integration in DevOps
Continuous Integration (CI) is a fundamental practice in DevOps that aims to improve software quality and speed up delivery. By integrating code changes frequently, teams can detect errors faster and reduce integration problems. This practice allows developers to focus on writing code rather than spending time on debugging and fixing issues later in the development cycle.
Continuous integration is not just a tool, but a mindset that allows teams to deliver software faster and with higher quality.
Imagine a band practicing together; the more often they rehearse, the tighter their performance becomes. Similarly, CI ensures that every code change is tested and integrated regularly, leading to a more cohesive product. This not only enhances collaboration among team members but also fosters a culture of shared responsibility for quality.
With CI, teams can deliver updates to users more frequently, providing a better experience. It lays the groundwork for further DevOps practices, such as Continuous Deployment (CD), where automated testing and deployment come into play, ensuring a smooth transition from development to production.
Key Benefits of Using CI Tools
Implementing CI tools comes with a multitude of benefits, the most notable being reduced time to market. Automated testing and integration processes mean that developers can identify issues sooner, which accelerates the delivery pipeline significantly. This efficiency not only saves time but also reduces the costs associated with late-stage bug fixes.
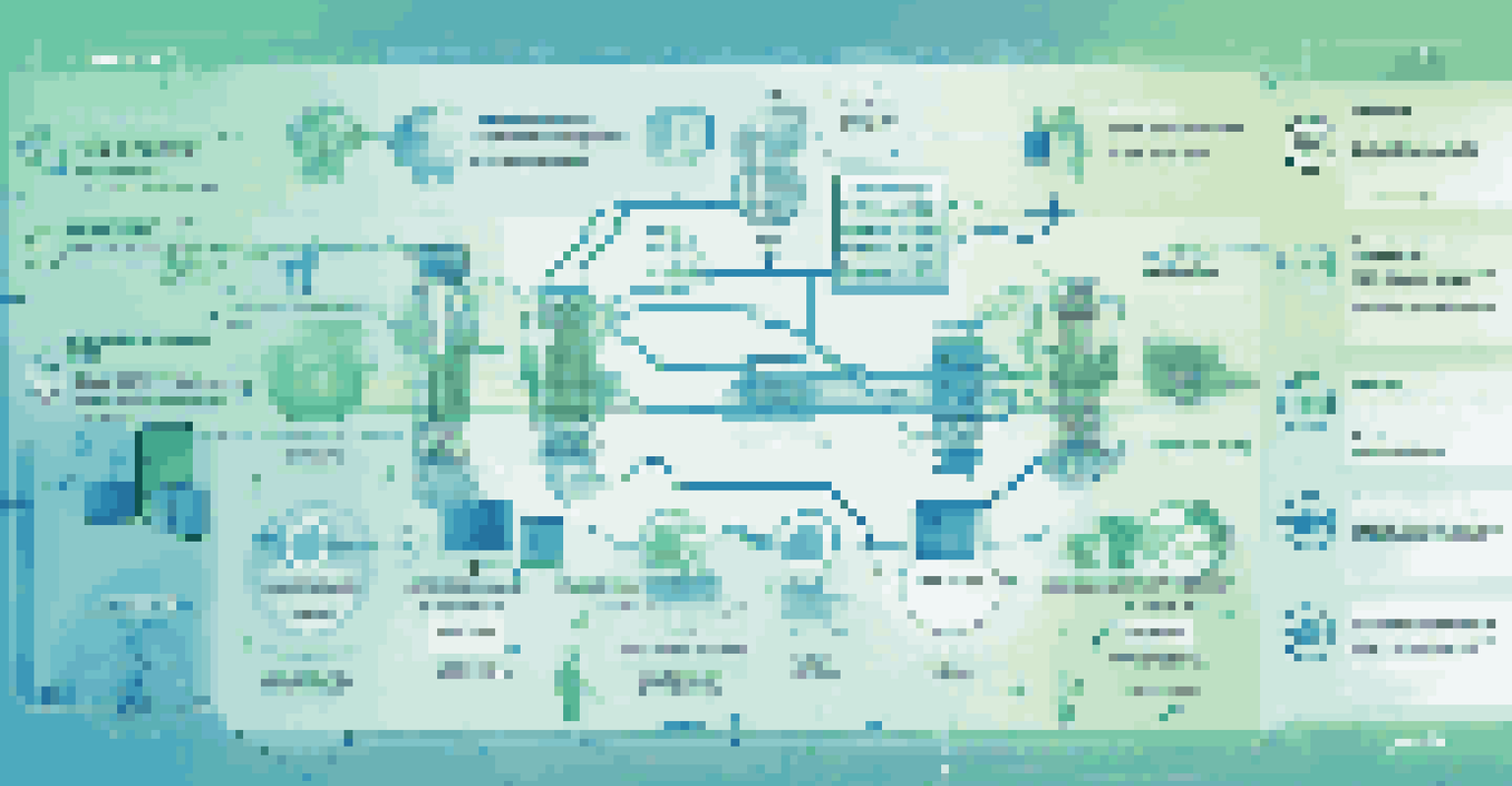
Another benefit is enhanced collaboration between teams, as CI tools provide a shared platform for code management. Developers can easily see others' changes, which promotes better communication and understanding within the team. It’s like having a shared whiteboard where everyone can contribute their ideas and updates, making the process more transparent.
Benefits of Continuous Integration
Implementing Continuous Integration (CI) leads to faster detection of errors, improved collaboration, and higher code quality.
Finally, CI tools help maintain a high standard of code quality. Through automated tests that run with each integration, teams can ensure that only code that meets the required standards gets deployed. This proactive approach to quality assurance minimizes the risk of defects in the production environment.
Popular CI Tools in the DevOps Landscape
There are several CI tools that have become staples in the DevOps community, each offering unique features. Jenkins is perhaps the most well-known CI tool, renowned for its flexibility and extensive plugin ecosystem. It allows teams to automate various tasks and integrate with numerous other tools, making it a favorite among developers.
The best way to predict the future is to implement it.
Another popular option is CircleCI, which simplifies the CI process with its cloud-based platform. It allows for quick setup and integrates seamlessly with GitHub and Bitbucket, enabling developers to focus more on coding rather than configuration. This ease of use is particularly appealing for smaller teams or startups looking to streamline their workflow.
GitLab CI/CD is also gaining traction, especially among teams already using GitLab for version control. Its built-in CI/CD capabilities mean that everything is managed in one place, which can significantly reduce complexity. This integration fosters a smoother workflow that aligns perfectly with the principles of DevOps.
Integrating CI Tools into Your Workflow
Integrating CI tools into your existing workflow may seem daunting, but it can be a straightforward process with the right approach. Start by selecting a tool that aligns with your team's needs and existing infrastructure. Consider factors like ease of use, integration capabilities, and support for your tech stack to ensure a smooth implementation.
Once you've chosen a CI tool, the next step is to set up your repository for automated builds. This typically involves configuring your version control system to trigger builds when code is pushed. Think of it as setting a domino effect in motion: one small change can set off a series of automated tests and deployments, ensuring everything runs smoothly.
Key CI Tools in DevOps
Popular CI tools like Jenkins, CircleCI, and GitLab CI/CD offer unique features that enhance automation and streamline workflows.
Finally, it's essential to foster a culture of continuous improvement. Encourage team members to communicate about the CI process and share feedback on how it can be enhanced. By treating CI as an evolving practice, your team can continuously refine its processes and tools to better meet its goals.
Common Challenges with CI Tools
While CI tools offer numerous advantages, they are not without their challenges. One common issue is the initial setup and configuration, which can be time-consuming and complex, especially for teams new to automation. Think of it like assembling a piece of furniture; it can be a hassle upfront, but the end result is worth it when everything fits together nicely.
Another challenge is maintaining the CI environment. As your codebase grows, it’s vital to regularly update and clean up your CI processes to prevent bottlenecks. Neglecting this can lead to longer build times and frustration among team members, much like clutter in a workspace can hinder productivity.
Lastly, integrating CI tools with existing workflows can sometimes create friction, especially if team members are resistant to change. It’s crucial to communicate the benefits clearly and provide adequate training to ease this transition. By addressing concerns upfront, you can foster a more positive outlook towards adopting CI.
The Role of Automation in CI Tools
Automation is the backbone of Continuous Integration, allowing for swift and reliable testing of code. With automated tests, developers can ensure that new changes do not break existing functionality, effectively catching bugs before they reach production. This is akin to having a vigilant guardian who checks everything before it goes out the door.
Moreover, automation not only speeds up the testing process but also enhances accuracy. Manual testing can often lead to human errors, whereas automated tests consistently execute the same way every time. This reliability is crucial in maintaining high-quality standards across software releases.
Future Trends in CI and DevOps
Emerging trends such as AI integration, cloud-native solutions, and a focus on security are shaping the future of CI tools and practices.
By automating repetitive tasks, teams can free up valuable time to focus on more strategic activities, such as feature development or improving user experience. In essence, automation empowers teams to be more innovative while ensuring their software remains robust and dependable.
Future Trends in CI Tools and DevOps
As technology evolves, so too does the landscape of CI tools and DevOps practices. One trend gaining momentum is the integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into CI processes. AI can analyze vast amounts of data quickly, helping teams to predict potential issues before they arise and optimize their CI/CD pipelines more effectively.
Another trend is the shift towards more cloud-native CI solutions that offer scalability and flexibility. As more teams adopt cloud technologies, the demand for CI tools that can seamlessly integrate with cloud services is on the rise. This shift allows organizations to scale their operations efficiently while reducing infrastructure management overhead.
Lastly, there’s a growing emphasis on security within the CI process, known as DevSecOps. Integrating security practices into the CI pipeline ensures that vulnerabilities are addressed early, making security a shared responsibility among all team members. This proactive approach not only protects the software but also builds trust with users.